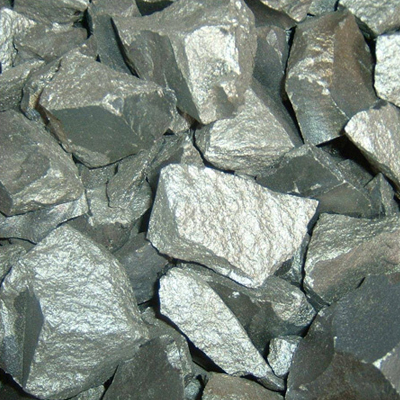
Silicomanganese (SiMn)
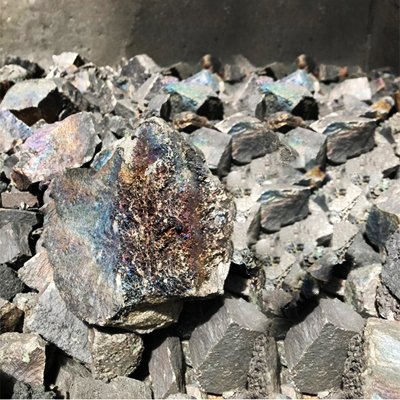

Ferromanganese (FeMn)
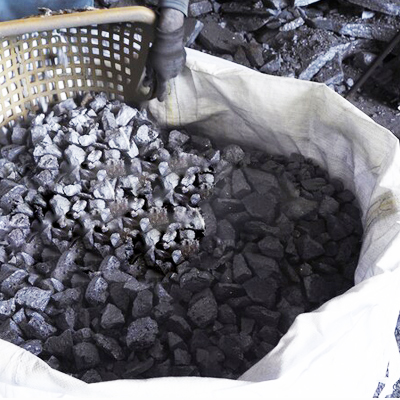

Ferrosilicon (FeSi)
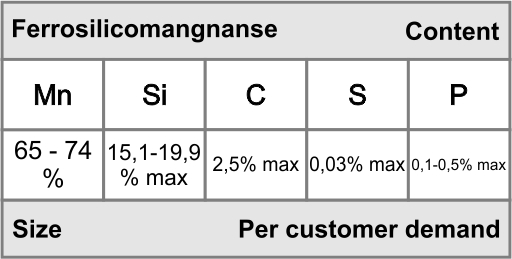
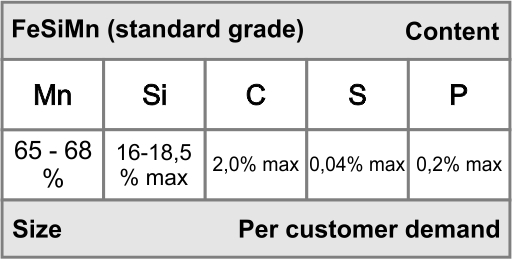
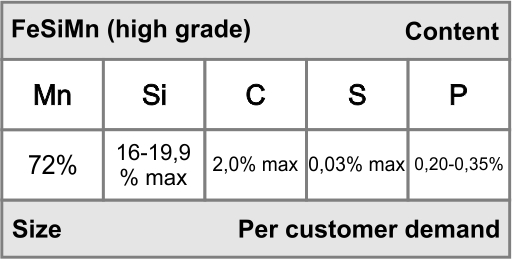
Silicomanganese (SiMn), a ferroalloy produced by smelting manganese ore and quartzite in the presence of coke in a submerged arc furnace. SiMn is used as both deoxidizer and for chemistry adjustment of silicon and manganese in iron and steel.
Ferromanganese (FeMn), a ferroalloy produced by smelting manganese ore in the presence of coke. FeMn can be produced in either a blast furnace or a submerged arc furnace. Ferromanganese is typically produced as High Carbon (78% Mn, 7.5% C), Medium Carbon (80% Mn, 1.5% C) and Low Carbon (80% Mn, 0.5% C). Ferromanganese is used as a strengthener in steel, or in combination with ferrosilicon as a deoxidizer.
Ferrosilicon (FeSi) is a ferroalloy produced by smelting quartzite with coke in presence of scrap iron or iron oxide in a submerged arc furnace. Identified by the amount of silicon contained, the most common varieties of ferrosilicon produced are 50%, 65% and 75%. FeSi can contain 1%-2% of calcium and aluminum with the balance of the product made up as iron. Ferrosilicon is used primarily as a deoxidizer. It readily combines with the oxygen in the molten metal. It is sometimes used as a degasifier because of its affinity for undesirable gases. FeSi is also commonly used as a source of silicon in cast iron. Ferrosilicon can be alloyed with additional metals in custom combinations for specialty uses in steel and iron industries.